How to Better Understand the Customer, Part 1. Customer Journey Mapping


Big Data makes it possible to track the customer journey from the moment of becoming familiar with the brand to the first purchase, re-selling and up-selling. This is a customer journey map (CJM), a global and strategic tool that helps you understand:
- How a company can enter a new market segment.
- How to increase an average receipt.
- How to attract new customers and retain old ones.
- How to increase conversion.
Well, what is the purpose of a map? The CJM format is convenient to study the behavior of your customers, research the audience of competitors, identify all points encouraging business growth, find and eliminate weaknesses in your marketing strategy. A customer journey map is suitable for companies that have already got their audience, constant traffic and information about their customers. Launching startups, you can use a customer journey map, but taking into account it will be based on hypotheses and on the analysis of the competitors’ audience. The CJM will be complemented with new data as the product develops.
The benefits of customer journey mapping:
- It helps to get interaction between the customer and the company and highlight all the stages that they go through. You can also use it to track changes in the customer journey after a product or service update.
- It allows the company staff to see the product through the eyes of customers.
- It clearly shows the strengths and weaknesses of the marketing strategy.
Getting ready for customer journey mapping
Before customer journey mapping, we define the goals and structure of the map. We need to set all the steps, stages and episodes that make up the customer journey. For this, we study three categories of people:
- Product users. We find out what influenced their choice and fix the problems they experience while interacting with the product.
- Closed lost customers. We find out why they decided to left.
- Customers of competitors. We figure out why the user chose another product and whether he knows about your brand, analyze the best and worst experience of competitors.
We pay special attention to the last two categories. The reasons why potential buyers left the brand or switched to competitors will be points encouraging business growth.
Before moving on to the study, let’s draw up a small plan that will help compile the necessary information.
1. Determining the customer decision-making logic
Here it is important to find answers to the following questions:
- How do they find out about the company?
- What services do they use to search for product information?
- How do they compare discovered offers?
- What factors besides price influence decision making?
2. Evaluating the customer's transition from one stage to another
It is important to estimate how long each stage of the customer journey takes. In other words, we evaluate how many minutes pass from the moment a customer has a goal to buy a product until the search for a suitable option and purchase. The stages that can be distinguished here:
- Showing up of the goal.
- Searching for suitable offers.
- Comparing with competitors.
- Contacting company manager.
- Making a purchase.
- Using of the product.
- Giving feedback.
- Re-selling or up-selling.
3. Identification of barriers arising during the customer journey
We collect data on what makes the customer feel negative emotions, what causes the difficulties and whether all this can influence the final decision. Possible barriers:
- Not user-friendly website interface.
- Problems with placing an order.
- Inappropriate payment terms.
- Long order delivery.
- Waiting when choosing a product.
- Poor communication with company managers.
- Lack of a product and its analogues.
Collecting information, refer to different sources. This way you will receive only reliable data about your customers and will be able to detail the buyer journey map as much as possible. Below we have got a list of the most important ones for you:
Don't be afraid to ask your customers questions. Using a consumer survey, you can find out first-hand what they like or dislike about your product. Ask what factors customers use to choose a particular product and what might turn them off. Surveys can be conducted via offline and online channels.
Using web analytics tools, you can track the customer actions on the site, find out more information about them or, for example, find out at what stage they stopped their journey.
Analyze the actions of subscribers in your social networks: what posts they most often like, what comments they write, and who they subscribe to besides you. Conduct polls in official communities or communicate with customers directly.
Contact sales managers and customer support. As a rule, these specialists often interact with buyers and have information about them.
Go through customer journey yourself and fix your goals, impressions, and barriers along the way. Thus, you will see the product through the eyes of the customer and understand the internal processes of the company.
Customer journey mapping
The customer journey map allows you to synchronize the actions of all customers and see the complete picture. Most often, they go the same way with a difference of several stages. It is best to put all clients or individual segments on the map.
The buyer journey map consists of three conventional zones:
- Customer zone. All available information about the customer is recorded here.
- Interaction zone. The intersection of customer and company zones.
- Company zone. The tools you use to interact with the customer.
Let's take an example of how to create a customer journey map correctly.
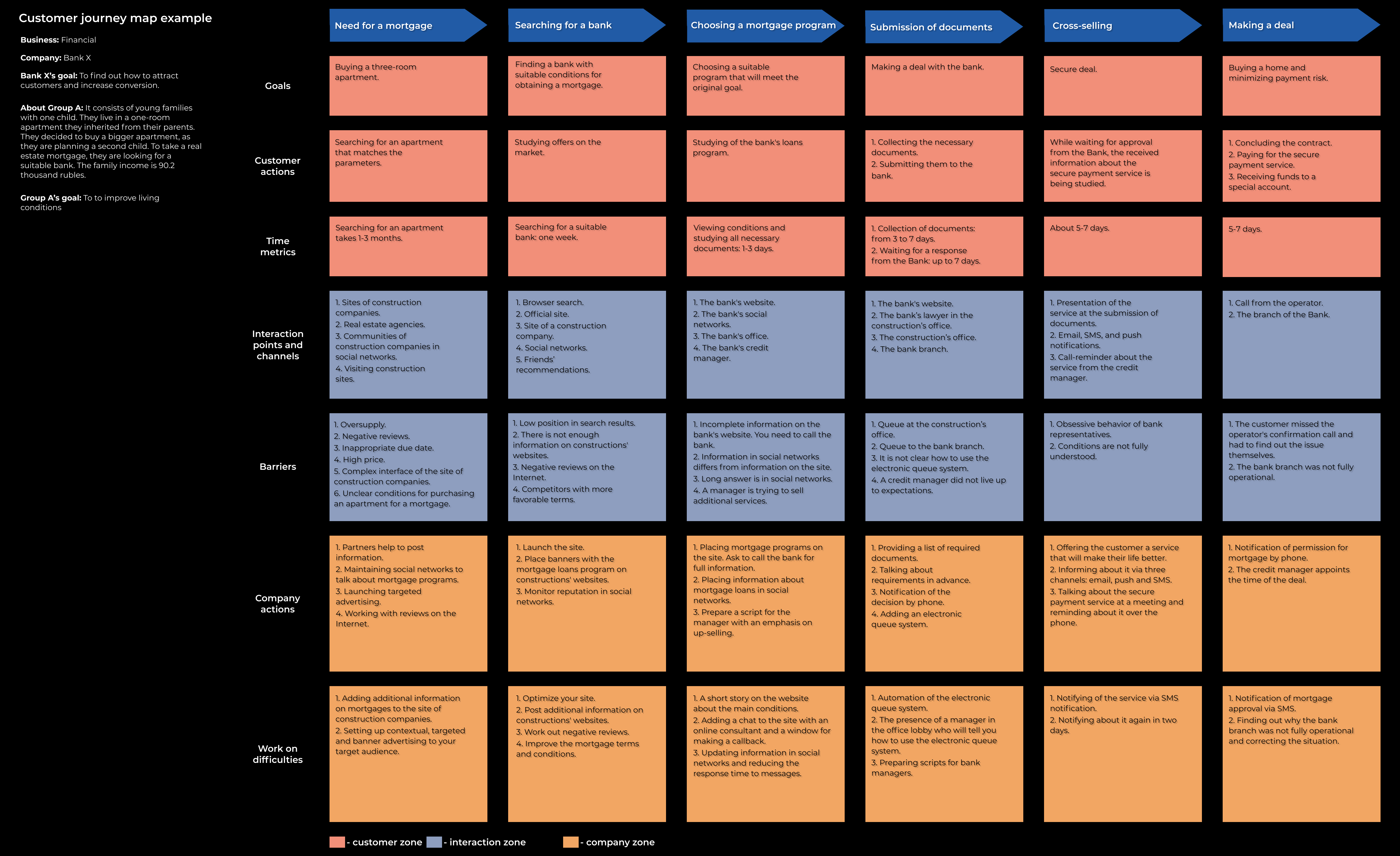
Bank X wants to attract customers and increase conversion. For this, it was decided to build a customer journey map to identify strengths and weaknesses in the marketing strategy. Analyzing the audience, 5 groups were identified. We will consider only one.
Group A consists of young families with one child. They live in a one-room apartment they inherited from their parents. They decided to buy a bigger apartment, as they are planning a second child. To take a real estate mortgage, they are looking for a suitable bank. The family income is 90.2 thousand rubles.
Map the goals and actions the customer wants to achieve. This data will help you better understand customer behavior at certain times.
Group A's goal is to improve living conditions. They need to choose an apartment and a bank that provides favorable mortgage terms.
This section of the map shows the time the client spends completing each stage in the journey. You can use them to identify difficulties and try to simplify the journey.
In our example, the young family spends the most time searching for their dream apartment — from 1 to 3 months. The bank will not speed up this stage, but it can prepare the ground for further interaction. For example, it can place information about mortgage loans on the websites of the partners, run contextual or targeted advertising.
Identify all interaction points between the customer and the company. Mark the ones where the customer most often comes into contact with the product. Depending on the interaction channel, the points can be offline or online. For example, a customer can view a product catalog from a computer, place an order through a mobile app, arrange delivery by phone, and leave feedback in the company's official social networks. Note even the interaction that did not take place or failed for some reason. Don't lose sight of your customers' actions. It is important to consider all options and put them on the customer journey map.
Our young family paid attention to the bank X thanks to targeted advertising in social networks. The main interaction point was the official website. At the same time, they receive additional information by phone and conclude the contract at the bank's branch.
Fix all barriers that prevent the user from moving from one stage to another. The barriers can be errors on the site, a malfunction in the mobile app, or getting the mailing list in spam. The difficulty can be not only technical: it may be an incorrect behavior of staff or the loss of customer interest in the product. Your main task is to find these barriers and develop methods to overcome them. The points where customers experience the most difficulties — critical. The main thing is to react in time and take measures to resolve the situation.
The main barriers of our clients are incomplete information on the bank's website and competitors with more favorable conditions. Because of the first critical point, they have to call the bank, find out all the conditions and listen to information about additional services that they are not interested in. Because of the second one, they have to choose from several offers.
This section of the map shows all the actions of the company in relation to the buyer. Many things you and your customer see differently, and that's okay. Considering both points of view, you can see where the difficulties arise and what contributes to this.
Here, for example, indicate what tools for attraction you use, how you behave in specific situations with clients.
Now you will hear the obvious thing, but if you want the customer journey to be as comfortable as possible, you need to get rid of the critical points and difficulties that we discussed above. Identify what is causing the barriers and work with the team to resolve them: fix technical problems, improve the site usability, and improve the product and service.
For example, to solve critical points, the bank will add more information about mortgage loans to the site and create a chat with an online consultant, so that customers do not have to find out additional questions by phone.
Conclusions
The customer journey map is not easy, but it's an extremely effective thing. We have collected all the steps to build a single checklist: peek, use, make up!
- Study product users, closed lost customers, and customers of competitors. Analyze the goals, problems, hobbies and behavior of your target audience.
- Divide the customer journey map into three zones: customer, company, and interaction.
- Put goals, actions, and time metrics in the customer zone.
- Mark the points and channels of interaction between the customer and the company, critical points and barriers in the interaction zone.
- Fix company actions and work on difficulties in the company zone.
- For convenience, use special customer journey mapping tools for visualization, which we talk about here.
Filling out the map, pay special attention to barriers and critical points. This will help you see the weak points in your communication strategy.
While you are mapping the customer journey, we are preparing the second part which will tell you how to automate the customer journey.
You might be interested in:
Choosing the right software can make the difference between success and failure, and that's what we're going to be looking into in this piece.
Read moreBy dividing the audience into segments, you can get ideas for business development and increase the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Read moreEnd-to-end analytics makes marketing manageable and completely transparent and saves the budget. You always know that you are investing in effective channels and the right actions.
Read more



