Anti-spam System (PTR, DKIM, SPF, FBL, DMARC)


There are different ways to fight against spam and cheaters. Before you receive an email, Email Service Providers check the reputation of a sender and analyse information in that email. To identify you as a sender correctly Email Service Providers use the following technologies and mechanics:
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM is a protection technology that lets an organization take responsibility for emails it sends. DKIM adds a digital signature that is connected with the sender’s domain. The signature is verified automatically by the recipient server.
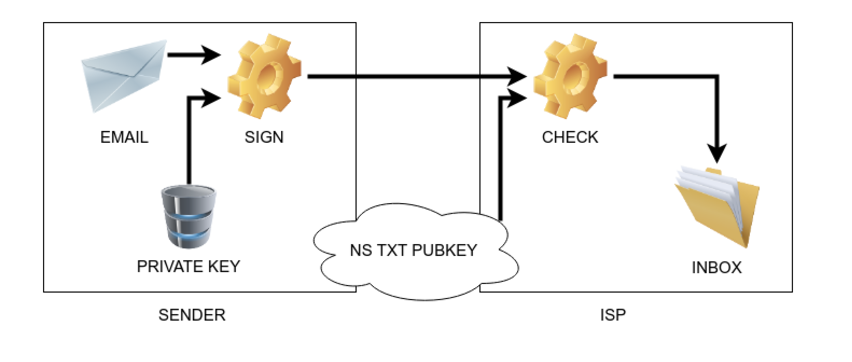
The signature is checked automatically. The recipient uses black and white lists to identify the sender’s reputation and decides whether to deliver this email or inform the sender about a mistake.
In order to use DKIM technology you’ll need:
- an email server, that has a function to sign outbound mails.
- to make a record in the DNS about DKIM support and a public key.
- private and public keys for email authentication.
RSA-SHA256 и RSA-SHA1 algorithms are mostly used in this technology. Recommended key length is 1024 bit.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
Sender policy framework conrolls sender domain identity and protects a domain from illegal usage. SPF adds to the sender domain a special TXT record, that identifies the policy of this domain sendings from different hosts.
In a ТХТ-record a domain owner points a list of servers that have the right to send emails on behalf of this domain and the way to treat emails that are sent from other servers.
Why is it necessary? Almost all antispam systems use three criteria to check the quality of sent mails:
- IP reputation check (more details in the article Inbox or junk folder: cause and effect).
- content check — theme, headlines, spamwords etc.
- DKIM digital signature check and SPF analysis of domain record.
| type | example |
|---|---|
SPF | spf2.0/pra include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all |
TXT | spf2.0/pra include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all |
TXT | v=spf1 include:spf.aksend.net ip4:A.B.C.D -all |
In this example, it is allowed to use hosts of spf.aksend.net domain, and A.D.C.D. IP addresses. Using Ip4 directive you can enumerate each IP and the whole subnet. -all uniquely specifies that sending from other hosts won’t be valid. If you want to enable sending from any hosts, use «+all» (not recommended). Command «dig» will help you to check the existence and content of SPF records
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance)
This is a technology that helps a receiver to deal with email fraud if SPF and DKIM report a mistake on the receiver’s behalf. It is created to protect against spam, phishing and malicious emails disguised as emails from popular ESPs. Being a domain owner you are to decide what to do with these emails.
Before DMARC setting it is necessary to:
- set a SPF record;
- set a DKIM-record.
If an email is recognised as a fake, rules for manipulating this data must be specified in the DNS of a domain. According to the stated criteria emails can be rejected by the email server, sent to spam or passed.
Examples of email policy:
1. Reject all emails that failed the check.
IN TXT "v=DMARC1; p=reject"
2. Reject all emails that failed DMARC check and send reports to the postmaster@exampledomain.com.
"v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=postmaster@exampledomain.com
3. 30% of emails sent by your domain but failed DMARC check go to quarantine.
"v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; pct=30"
FBL/CFL (FeedBack Loop)
It is a kind of lifetime feedback by which you can get reports on the users who press «report spam» in your certain email.
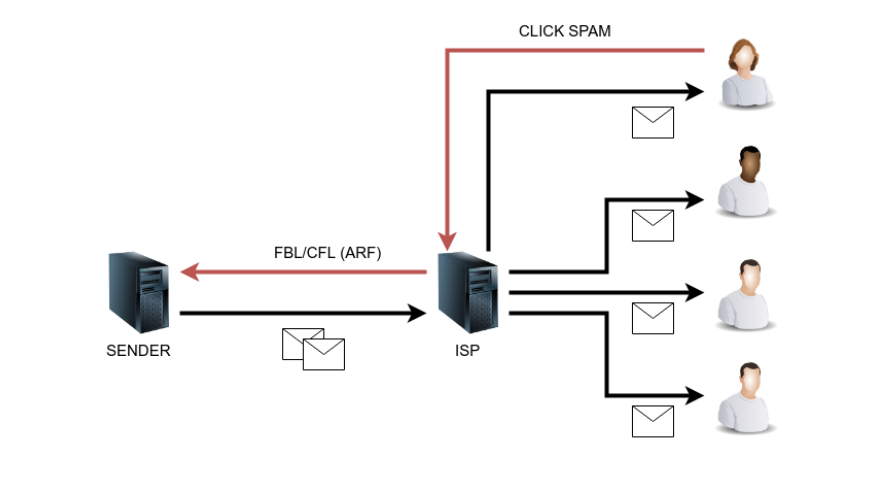
| Box | Purpose |
|---|---|
| abusemaster@domain | ARF automatic reports |
| postmaster@domain | Confirmation emails; necessary for FBL registration |
| abuse@domain | A box recommened by abuse.net |
PTR (Pointer)
PTR is a reversed DNS-record that connects IP address and your website domain. PTR-record is used for filtering of inbox mails. It adds reliability for the sending server and allows receiving end to check the hostname of an IP address.
An essential part of a complete setting of any sender is a setting of a reverse zone. Each sending IP must have such kind of zone and it should have a reference to the sender’s domain. The reverse zone is maintained by the owner of IP addresses. if it is not delegated to you, you need to send a request to the provider’s tech support to add or edit entries.
| Domen | Type | Record |
|---|---|---|
1.1.1.1.in-addr.arpa. | PTR | mx1.s1.example.com |
2.1.1.1.in-addr.arpa. | PTR | mx2.s1.example.com |
Note, that IP address in the domain name is reversed. It is necessary to delegate a subdomain to the end user.
You might be interested in:
Read about what will and won't work in 2022. Learn how to promote a blog on Instagram using free and paid promotion methods.
Read moreDiscovering ways to better know your customers for efficient work with them?
Read moreCreate a website, a chatbot or a mobile app without programming skills. Do you think it's impossible? Well, you need to learn more about low-code and no-code.
Read more



